Clinical dermatology is a specialised branch of medicine focused on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of skin, hair, and nail disorders. It encompasses a wide range of conditions, from common issues like acne and eczema to more complex diseases such as skin cancer and autoimmune disorders. With the skin being the largest organ of the human body, its care is paramount to overall health and well-being. This article delves into the core aspects of clinical dermatology, shedding light on its importance and scope in modern healthcare.
What is Clinical Dermatology?
Clinical dermatology involves the medical aspects of skin care. Unlike cosmetic dermatology, which focuses primarily on aesthetic concerns, clinical dermatology addresses medical conditions that affect the skin, hair, and nails. A clinical dermatologist is trained to diagnose and treat various skin disorders, ranging from minor rashes and infections to serious diseases that can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life.
Common Skin Conditions Treated in Clinical Dermatology
-
- Acne: One of the most prevalent skin conditions worldwide, acne affects millions of people, especially during adolescence. Clinical dermatologists provide treatments like topical creams, oral medications, and laser therapy to manage acne effectively and prevent scarring.
- Eczema: Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory condition that causes itchy, red, and dry skin. Dermatologists often recommend a combination of moisturizers, corticosteroids, and lifestyle changes to manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
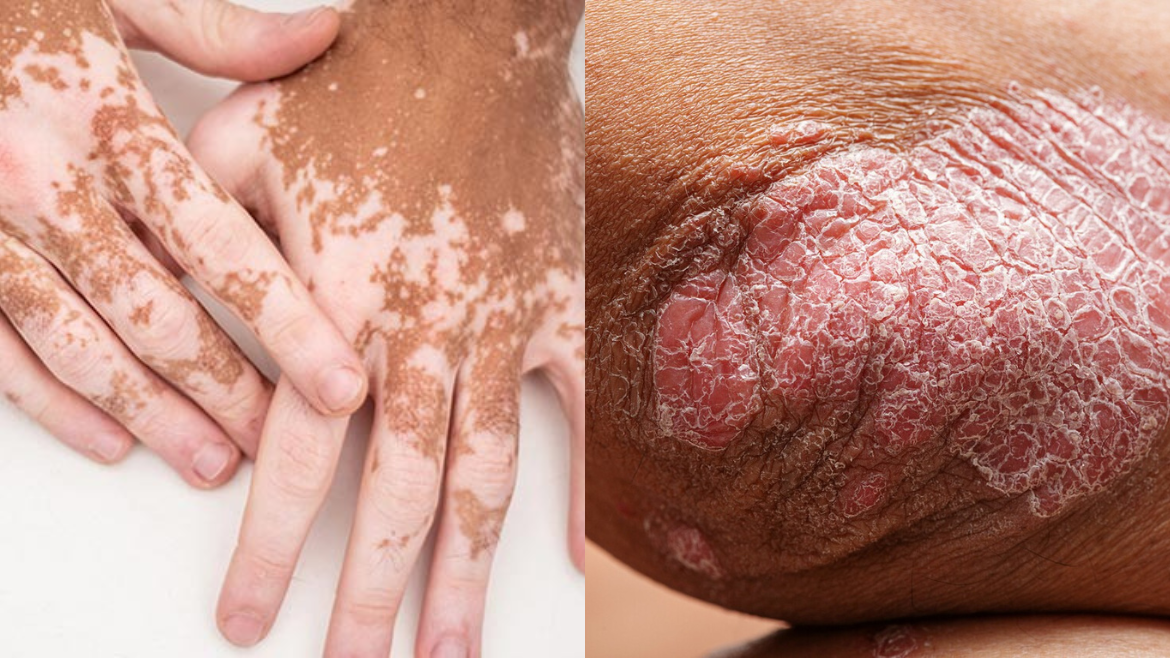
- Psoriasis: This autoimmune condition leads to the rapid buildup of skin cells, causing red, scaly patches that can be painful and itchy. Clinical dermatologists offer a variety of treatments, including topical therapies, systemic medications, and biologics to control psoriasis symptoms.
- Rosacea: This chronic skin condition is characterised by facial redness, visible blood vessels, and, in some cases, pus-filled bumps. Clinical dermatologists provide tailored treatments, such as topical medications, oral antibiotics, and laser therapy, to manage rosacea symptoms.
- Vitiligo: A skin disorder called vitiligo causes white spots to appear as a result of the pigment melanin, which gives skin its colour, being lost. Skin tone becomes uneven as a result of the destruction of melanocytes, the cells that produce pigment. It is controlled and not communicative.
Diagnostic Tools and Treatments in Clinical Dermatology
Clinical dermatology relies on a variety of diagnostic tools and treatments to manage skin conditions effectively. Some of the most common diagnostic methods include:
– Skin Biopsy: A small sample of skin is removed and examined under a microscope to diagnose various skin conditions, including skin cancer.
– Patch Testing: Used to identify allergens causing contact dermatitis by applying small amounts of potential allergens to the skin.
– Dermatoscopy: A non-invasive imaging technique that helps dermatologists examine skin lesions more closely to detect skin cancer early.
Treatment options in clinical dermatology can vary widely depending on the condition and its severity. Common treatments include topical creams and ointments, oral medications, phototherapy, and surgical procedures.
The Importance of Regular Dermatological Check-ups
Regular check-ups with a clinical dermatologist are essential for maintaining healthy skin and catching potential problems early. Early detection of skin conditions like melanoma can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes. Moreover, managing chronic skin conditions like eczema, psoriasis, and acne can significantly improve a patient’s quality of life.