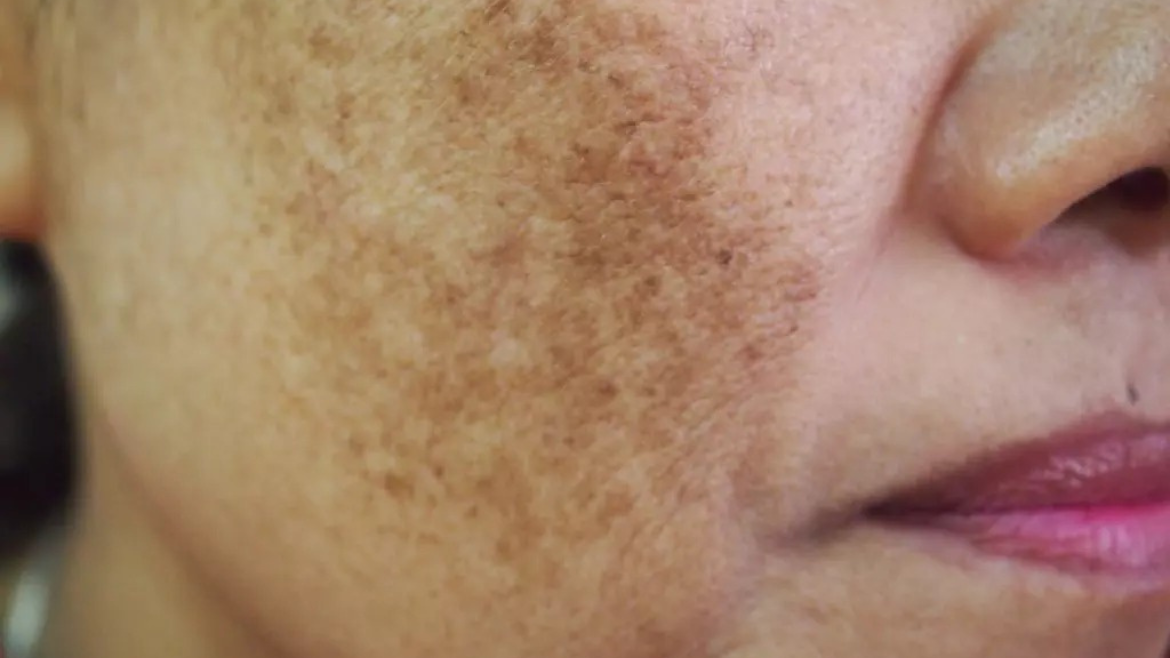
What is Melasma
Melasma is a common skin disorder that often affects the face and is characterized by dark, discolored patches. It happens when an excess of a pigment called melanin, which determines skin tone, builds up. Sun exposure, hormonal changes (typically during pregnancy) and certain medications are common factors. People with darker skin tones and women are more likely to suffer from melasma. Although it poses no health risks, its appearance can be modified with topical lotions, laser therapy and sun protection.
How Melasma Works
Although it can go deeper into the dermis, melasma mostly affects the epidermis, the topmost layer of the skin. The disorder is caused by overactivity of melanocytes, which are melanin-producing cells. Many things can contribute to this excessive activity:
Sun exposure: The sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays activate melanocytes, which increases the amount of melanin produced. As a result, melasma becomes more noticeable, especially in people with darker skin tones.
Hormonal changes: Melasma can be caused by hormonal changes, especially during pregnancy (often called the “mask of pregnancy”), menopause, or when taking birth control pills. Hyperpigmentation can result from an increase in melanin production caused by the hormones progesterone and estrogen.
Genetic predisposition: Having melasma in your family can make you more likely to have the disorder. Melasma is more common in certain ethnic groups, such as African, Asian, or Latin American groups.
Benefits of Treating Melasma
Melasma treatment can significantly improve quality of life and sense of self-worth. Melasma is not dangerous, although its effects on appearance can cause mental anguish. Fortunately, melasma can be effectively managed and reduced with a number of treatments:
Topical treatment: Hydroquinone, tretinoin, and corticosteroids are popular ingredients found in prescription creams used to lighten dark spots. These therapies work by promoting skin cell turnover and preventing melanin synthesis.
Chemical peels: In these, a solution is applied to the skin, which causes the outer layers to peel off, revealing younger and less pigmented skin. Chemical peels are a viable treatment option for epidermal melasma.
Laser therapy: Lasers are used to target and remove excess melanin in the skin. Deeper skin melasma can be effectively treated especially with fractional lasers.
Sun protection: To prevent melasma from worsening, use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF. Preserving the effects of previous treatments and preventing the appearance of new spots can be achieved with consistent sun protection.
Cosmetic Camouflage: Dark areas can be hidden with cosmetic products for individuals looking for quick results. These goods offer a temporary measure while more effective therapies are instituted.